git
설명
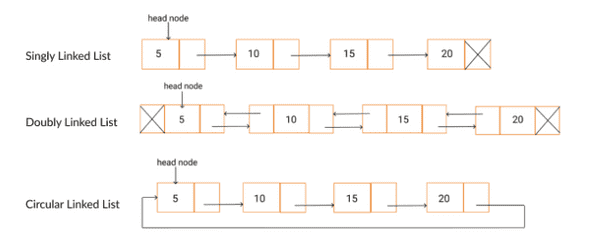
- 각 노드에 next, prev 포인터가 있어 이전, 다음 노드를 가르키는 구조
- 실행 시간에 메모리를 할당, 해제 가능한 동적 자료구조
(배열은 고정된 크기를 갖는다.)
구조
time complexity
구현 List
node
class DoublyLinkedListNode {
constructor(data) {
this.data = data;
this.next = null;
this.prev = null;
}
}DoublyLinkedList
class DoublyLinkedList {
constructor(data) {
this.head = null;
this.tail = null;
this.size = 0;
}
}insert
구현 리스트
* 7.2.1 원하는 위치항목 삽입하기 - insert
* 7.2.2 헤드에 항목 삽입하기 - insertAtHead
* 7.2.3 테일에 항목 삽입하기 - insertAtTail class DoublyLinkedList {
insert(position, value) {
//범위외의 값 체크
if (position >= 0 && position <= this.size) {
let newNode = new DoublyLinkedListNode(value),
currNode = this.head,
prevNode,
nextNode, // 명시적인 이해를 위해서 추가
index = 0;
/*
아래 3가지 조건일때 추가한는 로직이 다름
1. head에 추가
1.1 size가 0인 경우
1.2 size가 0이 아닌 경우
2. tail에 추가
3. !(head || tail): value를 Node를 순회한다.
*/
if (position === 0) {
//1. head
this.insertAtHead(value);
} else if (position === this.size) {
//2. tail
this.insertAtTail(value);
} else {
//3. !(head || tail): value를 Node를 순회한다.
//position 바로 직전까지 순회하면서 prevNode, nextNode 이동
while (index++ < position) {
prevNode = currNode;
currNode = currNode.next;
}
nextNode = currNode;
newNode.next = nextNode;
prevNode.next = newNode;
nextNode.prev = newNode;
newNode.prev = prevNode;
}
this.size++;
return true;
} else {
// else statement of 범위체크 if statement
return false;
}
}
insertAtHead(value) {
if (this.head === null) {
this.head = new DoublyLinkedListNode(value);
this.tail = this.head; // [A] ref.
} else {
const newNode = new DoublyLinkedListNode(value);
newNode.next = this.head;
this.head.prev = newNode;
// 0. this.head, this.tail을 callbyreference로 연결 되어 있다.
// 1. this.head.prev는 this.Tail의 prev프로퍼티 제일 마지막 위치다. 그래서 this.head.prev는 this.Tail의 제일 끝 노드의 prev다.
// 2. 1 -> 2 -> 3 이있을때 Tail의 prev 속성으로 프린트 하면 다음과 같다. 3 -> 2 -> 1
// this.head는 1이다. 여기에 this.head.prev에 값을 연결하면 1다음에 연결되는 것이다.
this.head = newNode;
}
this.size++;
}
insertAtTail(value) {
if (this.tail === null) {
this.tail = new DoublyLinkedListNode(value);
this.head = this.tail;
} else {
const newNode = new DoublyLinkedListNode(value);
newNode.prev = this.tail;
this.tail.next = newNode; // === this.tail.prev = newNode; (callbyreference 때문) <-[A] ref.
this.tail = newNode;
}
this.size++;
}
}remove - recursive
- recursive, node value 기준으로 제거
-
구현 리스트
* 7.2.4 원하는 위치항목 삭제하기(recursive - node value 기준) - delete - Node 값 기준으로 삭제 - recursiveDelFromHead, recursiveDelFromTail 호출로 Head, Tail 제거 * 7.2.4.1 헤드의 항목 삭제하기 - recursiveDelFromHead * 7.2.4.2 테일의 항목 삭제하기 - recursiveDelFromTail
class DoublyLinkedListNode {
constructor(data) {
this.data = data;
this.next = null;
this.prev = null;
}
// Node 값 기준으로 삭제
// DoublyLinkedList constructor에 head, tail이 있기 때문에 두개 메소드 호출로 각각 data를 삭제해준다.
delete(value) {
this.recursiveDelFromHead(this.head, value);
this.recursiveDelFromTail(this.tail, value);
}
recursiveDelFromHead(node, value) {
let currNode = node;
if (currNode.data === value) {
if (!currNode.prev) {
this.head = currNode.next;
this.head.prev = null;
return currNode.value;
} else if (!currNode.next) {
let returnValue = currNode.value;
currNode = null;
return returnValue;
} else {
currNode.prev.next = currNode.next;
currNode.next.prev = currNode.prev;
}
this.size--;
return currNode.data;
}
if (currNode.next === null) return null;
if (currNode.next) this.recursiveDelFromHead(currNode.next, value);
}
recursiveDelFromTail(node, value) {
let currNode = node;
if (currNode.data === value) {
if (!currNode.prev) {
this.tail = currNode.prev;
this.tail.prev = null;
return currNode.value;
} else if (!currNode.next) {
let returnValue = currNode.value;
currNode = null;
return returnValue;
} else {
currNode.prev.next = currNode.next;
currNode.next.prev = currNode.prev;
}
this.size--;
return currNode.data;
}
if (currNode.prev === null) return null;
if (currNode.prev) this.recursiveDelFromTail(currNode.prev, value);
}
}remove - iterator
- iterator, node position 기준으로 제거
-
구현 리스트
* 7.2.5 원하는 위치항목 삭제하기(loop - node position 기준) - deleteAt - Node 위치 기준으로 삭제 - deleteAtHead, deleteAtTail 호출 * 7.2.5.1 헤드의 항목 삭제하기 - deleteAtHead * 7.2.5.2 테일의 항목 삭제하기 - deleteAtTail
class DoublyLinkedListNode {
constructor(data) {
this.data = data;
this.next = null;
this.prev = null;
}
// Node 위치 기준으로 삭제
deleteAt(position) {
if (position > -1 && position <= this.size) {
let currNode = this.head,
prevNode,
index = 0;
if (position === 0) {
this.deleteAtHead();
} else if (position === this.size) {
this.deleteAtTail();
} else {
while (index++ < position) {
prevNode = currNode;
currNode = currNode.next;
}
prevNode.next = currNode.next;
currNode.next.prev = prevNode;
this.size--;
}
return currNode.value;
} else {
return null;
}
}
deleteAtHead() {
let toReturn = null;
if (this.head !== null) {
toReturn = this.head.data;
if (this.tail === this.head) {
//node가 하나 밖에 없는 경우
this.head = null;
this.tail = null;
} else {
this.head = this.head.next;
this.head.prev = null;
}
}
this.size--;
return toReturn;
}
deleteAtTail() {
let toReturn = null;
if (this.tail !== null) {
toReturn = this.tail.data;
if (this.tail === this.head) {
this.head = null;
this.tail = null;
} else {
this.tail = this.tail.prev;
this.tail.next = null;
}
}
this.size--;
return toReturn;
}
}find value
* 7.2.6 원하는 value 찾기 (head로 부터) - findStartingHead
* 7.2.7 원하는 value 찾기 (tail로 부터) - findStartingTail class DoublyLinkedListNode {
constructor(data) {
this.data = data;
this.next = null;
this.prev = null;
}
findStartingHead(value) {
let currentHead = this.head;
while (currentHead.next != null) {
if (currentHead.data == value) {
return true;
}
currentHead = currentHead.next;
}
return false;
}
findStartingTail(value) {
let currentHead = this.tail;
while (currentHead.prev) {
if (currentHead.data == value) {
return true;
}
currentHead = currentHead.prev;
}
return false;
}
}