javascript언어는 prototype을 기반으로 oop를 구현하고 있다. (클래스 기반의 oop를 구현한 언어도 있다.) prototype 기반의 언어가 어떻게 oop를 구현 하고 있는지 알아보도록 하자.
1 프로토타입의 개념 이해
1-1 constructor, prototype, instance
1-2 constructor 프로퍼티
2 프로토타입 체인
2-1 메서드 오버라이드
2-2 프로토타입 체인
2-3 객체 전용 메서드의 예외사항
2-4 다중 프로토타입 체인1 프로토타입의 개념 이해
1-1 Constructor, prototype, instance
-
Constructor
- A function that initializes an object
- similar to normal java constuctor
-
prototype
- Constructor의 property
- instance의 property __proto__과 메모리 공유
: constructor.prototype === instance.__proto__
-
instance
- Constructor를 new키워드로 호출로 생성한 객체
-
- 왼쪽 꼭짓점: Constructor(생성자 함수)
- 오른쪽 꼭짓점: Constructor.prorotype 프로퍼티
- new를 통해 instance 생성
- instance.__proto__
-
어떤 생성자 함수(Constructor)를 new 연산자와 함께 호출하면
- Constructor에서 정의된 내용을 바탕으로 새로운 인스턴스(instance)가 생성됩니다.
- 이때 instance에는 __proto__라는 프포퍼티가 자동으로 부여
- 이 프로퍼티는 Constructor의 prototype이라는 프로퍼티를 참조
-
prototype 개념의 핵심: prototype 프로퍼티, __proto__라는 프로퍼티
- prototype은 객체
- 이를 참조하는 __proto__도 객체
- prototype 객체 내부에는 인스턴스가 사용할 메서드를 저장
- 그러면 인스턴스에서도 숨겨진 프로퍼티인 __proto__를 통해서 이 메서들을 접근할 수 있게 된다.
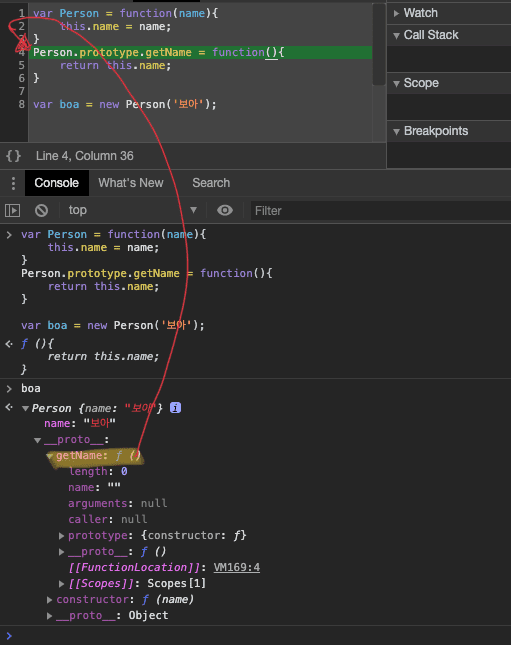
예제1 객체 type과 prototype, proto 관계
- {getName: f, constructor: f} -> constructor는 위 Person function 입니다.
-
new 키워드로 생성한 인스턴스 proto는 Person의 prototype에 의해서 생성한 것입니다.
var Person = function(name) { this._name = name; } Person.prototype.getName = function(){ return this._name; } typeof Person // function typeof new Person('boa'); // object new Person('boa'); // Person {_name: 'boa'} Person.prototype === new Person('boa').__proto__ // true Person.prototype //{getName: ƒ, constructor: ƒ} new Person('boa').__proto__ //{getName: ƒ, constructor: ƒ}
예제2 인스턴스와 인스턴스 __proto__ 의 실행컨텍스트
boa.getName === boa.__proto__.getName 은 같지만 getName을 수행할때 "실행컨텍스트"가 다르기 때문에 결과가 다르다
-
boa, boa.__proto__ 객체 비교
- boa => Person {_name: "boa"}
- boa.__proto__ => {getName: ƒ, constructor: ƒ}
-
boa.getName();
- return value => "boa"
- boa.getName return value => Person {_name: "boa"}
-
boa.__proto__.getName()
- return value => undefined
- boa.getName return value => Person {_name: "boa"}
- boa.__proto__ return value => {getName: ƒ, constructor: ƒ}
- boa._proto__에 _name 프로퍼티가 없어 식별자(this.name)를 찾을 수 없다.
- getName의 실행 컨텍스트는 boa._proto__(name은 boa 객체 하위에 있다.)
var Person = function(name) { this._name = name; } Person.prototype.getName = function(){ return this._name; } var boa = new Person('boa'); boa.getName(); // boa boa.__proto__.getName(); // undefined boa.getName === boa.__proto__.getName //true
예제3 prototype, __proto__관계
- boa의 property '__proto__'객체(Constructor function의 prototype으로 생성)는 "Constructor function의 객와 는 메모리를 공유하고 있다.
-
instance.__proto__, Constructor.prototype 객체는 메모리를 공유
- instance.__proto__ 변경하면 Constructor.prototype도 변경이 된다.
- Person.prototype === boa.__proto__; // true
var Person = function(name) { this._name = name; } Person.prototype.getName = function(){ return this._name; } var Person = function(name) { Person.prototype === boa.__proto__; // true
예제4 __proto__에서 getName 호출
-
boa.__proto__.getName() 에 의해서 호출된 getName의 실행컨텍스트(getName에서 this)
- => "boa.__proto__"
var Person = function(name) { this._name = name; } Person.prototype.getName = function(){ return this._name; } var boa = new Person('boa'); boa.__proto__._name = 'boa.__proto__'; boa.__proto__.getName(); //boa__proto__
예제5 prototype chain 예시
- boa객체 바로 하위에는 getName가 없을때는 __proto__ 객체에 getName 여부 확인을하고 호출한다. 이게 바로 prototype chanin 이다.
- rototype chanin원리에 따라서 __proto__에 없을경우 __proto__의 __proto__에 접근해서 찾게 된다.
-
boa.__proto__.getName
- = boa(.__proto__).getName
- = boa.getName
var Person = function(name) { this._name = name; } Person.prototype.getName = function(){ return this._name; } var boa = new Person('boa'); boa.getName(); // boa boa.__proto__.getName === boa.getName // true
예제6 function의 prototype과 인스턴스의 __proto__의 관계
- Constructor.prototype === instance.__proto__
var Constructor = function(name) {
this.name = name;
console.log(this);
}
Constructor.prototype.method = function(){};
Constructor.prototype.prototype1 = 'constructor Prototype property';
var instance = new Constructor('INSTANCE');
console.dir(Constructor);
console.dir(instance);예제7 Array 내장 생성자 함수로 알아본 prototype
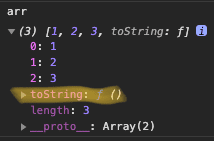
- var arr = [1,2]; 은 내장 생성자 함수 Array로 생성한 인스턴스다.
- 내장 생성자 함수 Array를 console.dir(Array) 하면 내부에 프로퍼티 확인 가능하다
- Array.prototype은 인스턴스로 만든 arr에서 사용할 수 있는 함수들이다.
var arr = [1,2];
console.dir(arr); //(2) [1, 2]
console.dir(Array); //Array: 내장 생성자 함수
Array.isArray(arr); //true: isArray는 Array내장 생성자함수의 함수다.
arr.isArray() //TypeError: arr.isArray is not a function
Array.prototype === arr.__proto__ //true1-2 constructor 프로퍼티
var arr = [1, 2]
Array.prototype.constructor === Array
arr.__proto__.constructor === Array
arr.constructor === Array
var arr2 = new arr.constructor(3, 4)
console.log(arr2) //[3,4]var Person = function(name) {
this.name = name
}
var p1 = new Person("인간1") //Person {name:"인간1"} true
var p1Proto = Object.getPrototypeOf(p1)
var p2 = new Person.prototype.constructor("인간2") //Person {name:"인간2"} true
var p3 = new p1Proto.constructor("인간3") //Person {name:"인간3"} true
var p4 = new p1.__proto__.constructor("인간4") //Person {name:"인간4"} true
var p5 = new p1.constructor("인간5") //Person {name:"인간5"} true
[p1, p2, p3, p4, p5].forEach(function(p) {
console.log(p, p instanceof Person)
})위 예제를 통해서 아래내용이 성립한다.
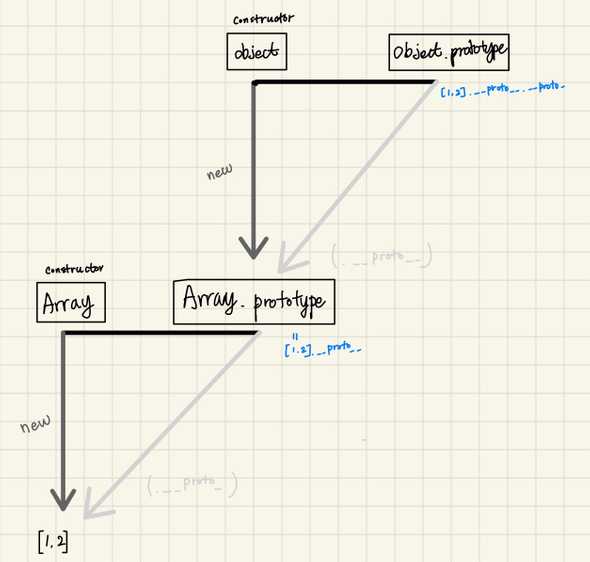
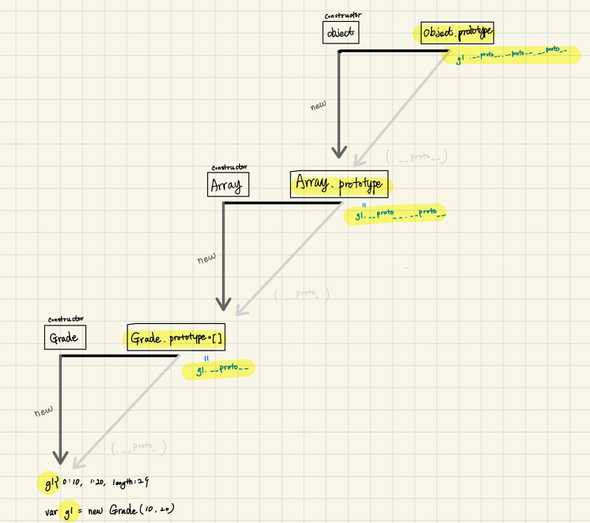
- 프로토타입 도식
-
Constructor, instance의 관계
// 아래 각줄은 모두 같은 대상을 가르킨다. [Constructor] [instance].__proto__.constructor [instance].constructor Object.getPrototypeOf([instance]).constructor [Contsructor].prototype.constructor // 아래 각줄은 동일한 객체(prototype)에 접근할 수 있습니다. [Constructor].prototype [instance].__proto__ [instance] Object.getPrototypeOf([instance])
2 프로토타입 체인
2-1 메서드 오버라이드
-
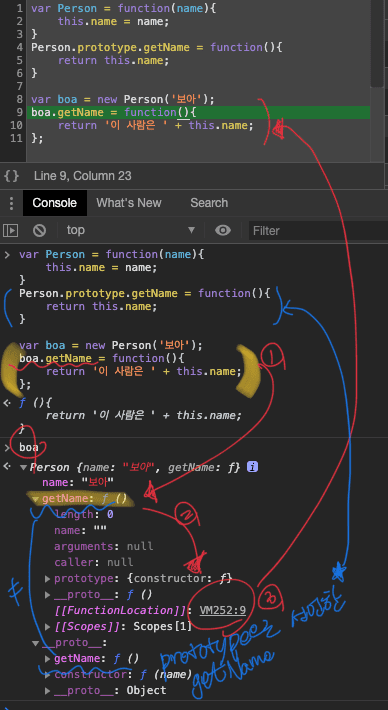
예제
- 아래 메서드 오버라이드 전, 후 캡쳐 참고
var Person = function(name) { this.name = name } Person.prototype.getName = function() { return this.name } var boa = new Person("보아") boa.getName = function() { return "이 사람은 " + this.name } console.log(boa) // Person {name: "보아", getName: ƒ} console.log(boa.getName()) // 이 사람은 보아 console.log(boa.__proto__.getNam()) // undefined Person.prototype.name = "권보아" console.log(boa.__proto__) // {name: "권보아", getName: ƒ, constructor: ƒ} console.log(boa.__proto__.getName()) // 이사람은 권보아 console.log(boa.__proto__.getName.call(boa)) // this를 명시적으로 선언 /* 메서드가 오버라이드된 경우에는 자신으로부터 가장 가까운 메서드에만 접근 그다음으로 가까운 __proto__의 메서드도 우회적인 방법을 통해서 접근 가능 */ -
결과
2-2 프로토타입 체인
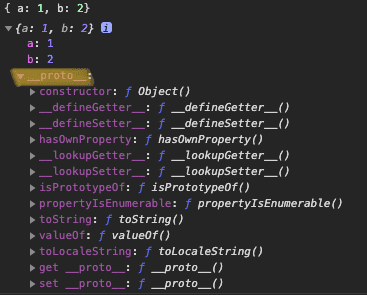
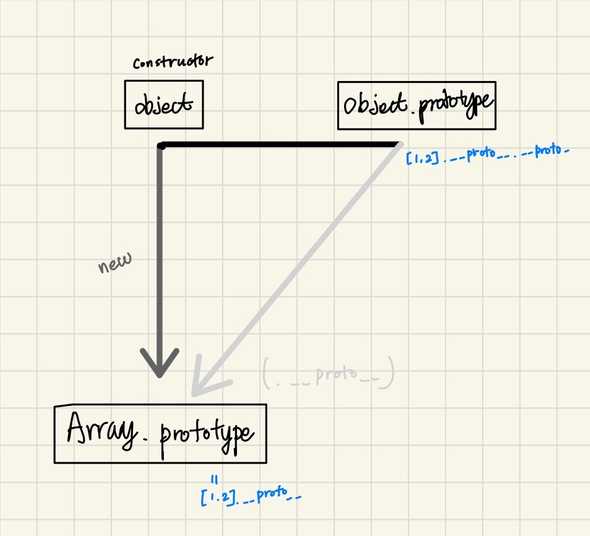
- Object의 내부 구조
- Array의 내부 구조
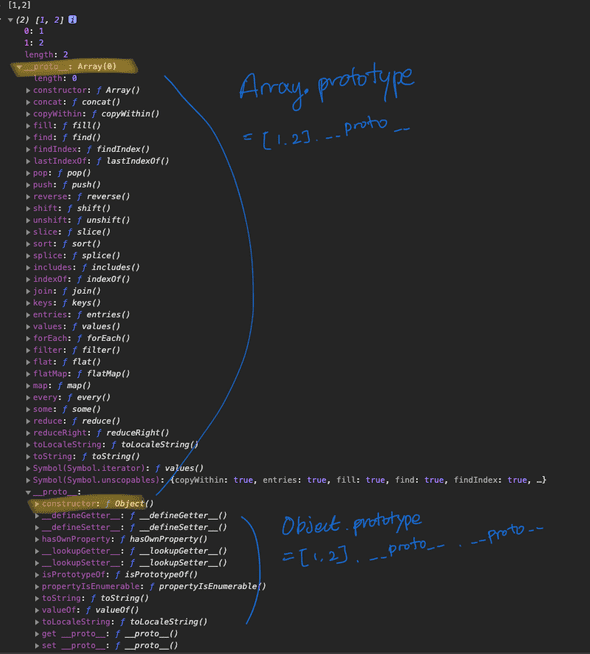
-
- [1,2]는 Array.prototype, Object.prototype내부의 메서드를 자신의 것처럼 실행 할 수 있다.
- .__proto__는 생략 가능하다 - 예시
var arr = [1,2]; arr(.__proto__).push(3); //3 arr(.__proto__)(.__proto__).hasOwnProperty(2); //true - 메서드 오버라이드와 프로토타입 체이닝
var arr = [1, 2, 3]
Array.prototype.toString.call(arr) //1,2,3
Object.prototype.toString.call(arr) //[object Array]
arr.toString() //1,2,3
arr.toString = function() {
//결과 아래 캡쳐 참고
return this.join("_")
}
arr.toString() //1_2_32-3 객체 전용 메서드의 예외사항
-
Object.prototyp에 추가한 메서드의 접근
Object.prototype.getEntries = function() { var res = [] for (var prop in this) { if (this.hasOwnProperty(prop)) { res.push([prop, this[prop]]) } } return res } var data = [ ["object", { a: 1, b: 2, c: 3 }], ["number", 345], ["string", "abc"], ["boolean", false], ["func", function() {}], ["array", [1, 2, 3, 4]], ] data.forEach(function(d) { console.log(d[1].getEntries()) })- 어떤 데이터 타입이건 거의 무조건 프로토타입 체이닝을 통해 getEntries 메서드에 접근
-
스태틱 메서드(객체한정메서드)
- 객체만을 대상으로 동작하는 객체 전용메서드들은 부득이 Object.prototype이 아닌 Object에 스태틱 메서드(static method)로 부여할 수 밖에 없다.
- 생성자 함수인 Object, 인스턴스 객체 리터럴 사이에는 this를 통한 연결이 불가능
- 전용 메서드 처럼 '메서드명 앞의 대상이 곧 this'가 되는 방식대신
this의 사용을 포기하고 대상 인스턴스를 인자로 직접 주입해야 하는 방식으로 구현
: 예시 Object.freeze({prop: 42}) - Object.prototype.consructor 하위 메서드 & Object.protptype 하위 메서드

2-4 다중 프로토타입 체인
아래 예제 주석 부분의 POINT 부분 이해부터 봐보자!
Grade.prototype에 Array instance를 세팅으로 g1(Grade function의 instance)에서 push를 사용할 수 있게 된다.
이렇게 새롭게 만드는 생성자 함수에 __proto__를 연결해서 체인 관계를 만들수 있다.
-
Grade 생성자 함수와 인스턴스 예제
var Grade = function() { //arguments: 유사배열 var args = Array.prototype.slice.call(arguments) for (var i = 0; i < args.length; i++) { this[i] = args[i] } this.length = args.length } var g = new Grade(100, 80) g.push(1) //Uncaugh TypeError: g.push is not function //POINT Grade.prototype = new Array() // == Grade.prototype = new Array().__proto__ // new Array() == []; //[].__proto__ === new Array().__proto__ //[] instanceof Array => true var g1 = new Grade(10, 20) g1.push(1) console.log(g1) //Grade(3) [10, 20, 1] g1.shift() console.log(g1) //Grade(3) [20, 1]
참고
- 코어 자바스크립트 - 위키북스
- 인사이드 자바스크립트
- 자바스크립트 완벽 가이드